True Limpets of the Lottiidae Family have shells that are flattened cone shaped that has an open, oval base. They do not have holes or slits along their margin or at their apex. The muscles scar inside a limpet shell is horseshoe shaped, with the opening toward the anterior. The interior of the shells is not iridescent. True Limpets have a head and a foot, but lack eyes and rely on chemoreceptors to navigate their surroundings. They have a muscular foot that enables them to cling to rocks and plants. Limpets are mobile but often return to the same home base. True Limpets are found globally and are amount the most common mollusks that are found in the intertidal zone to depths up to 30 m (100 feet). They consume algae, which they scrape from the rock with their radula. In turn they are preyed upon by shore birds, crabs, fish and sea stars. There are one hundred twenty species in the Lottidae Family of which twnety-five are found in coastal waters of Baja.
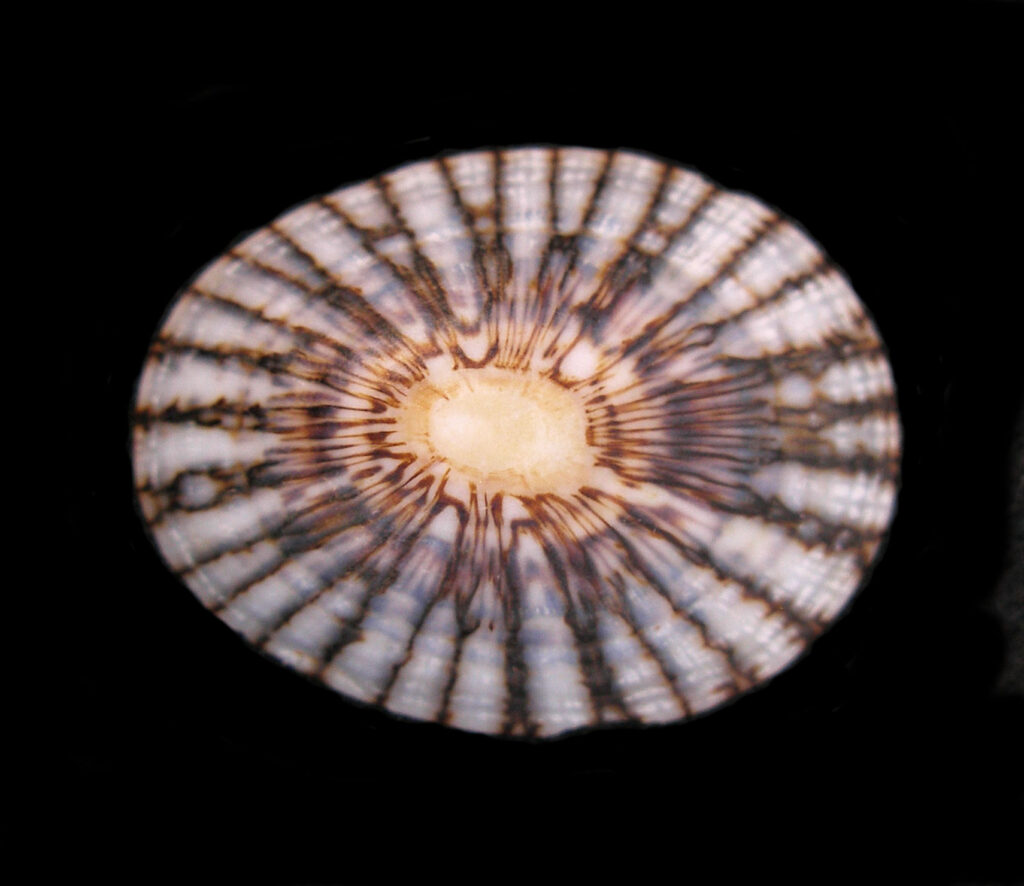
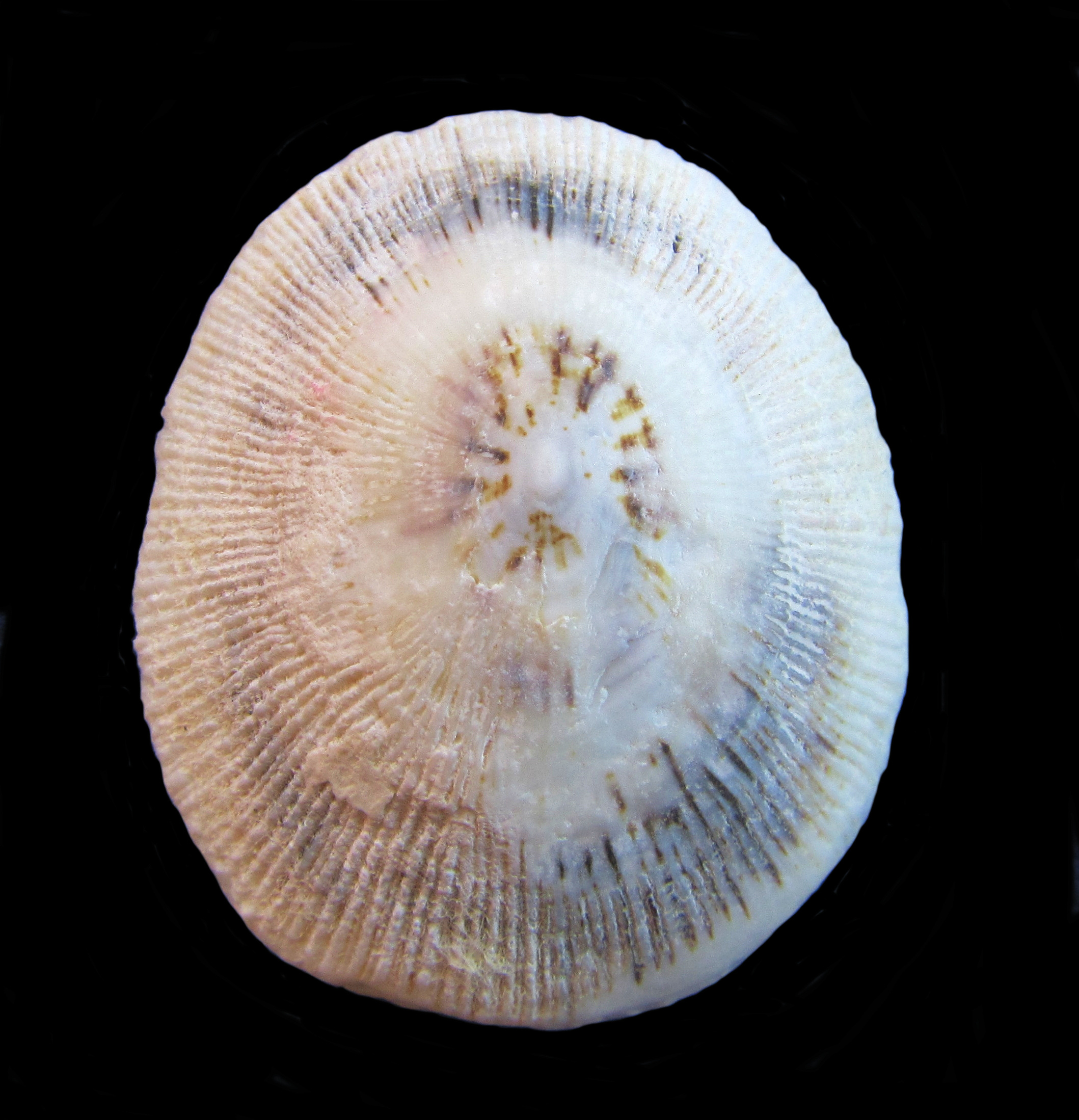


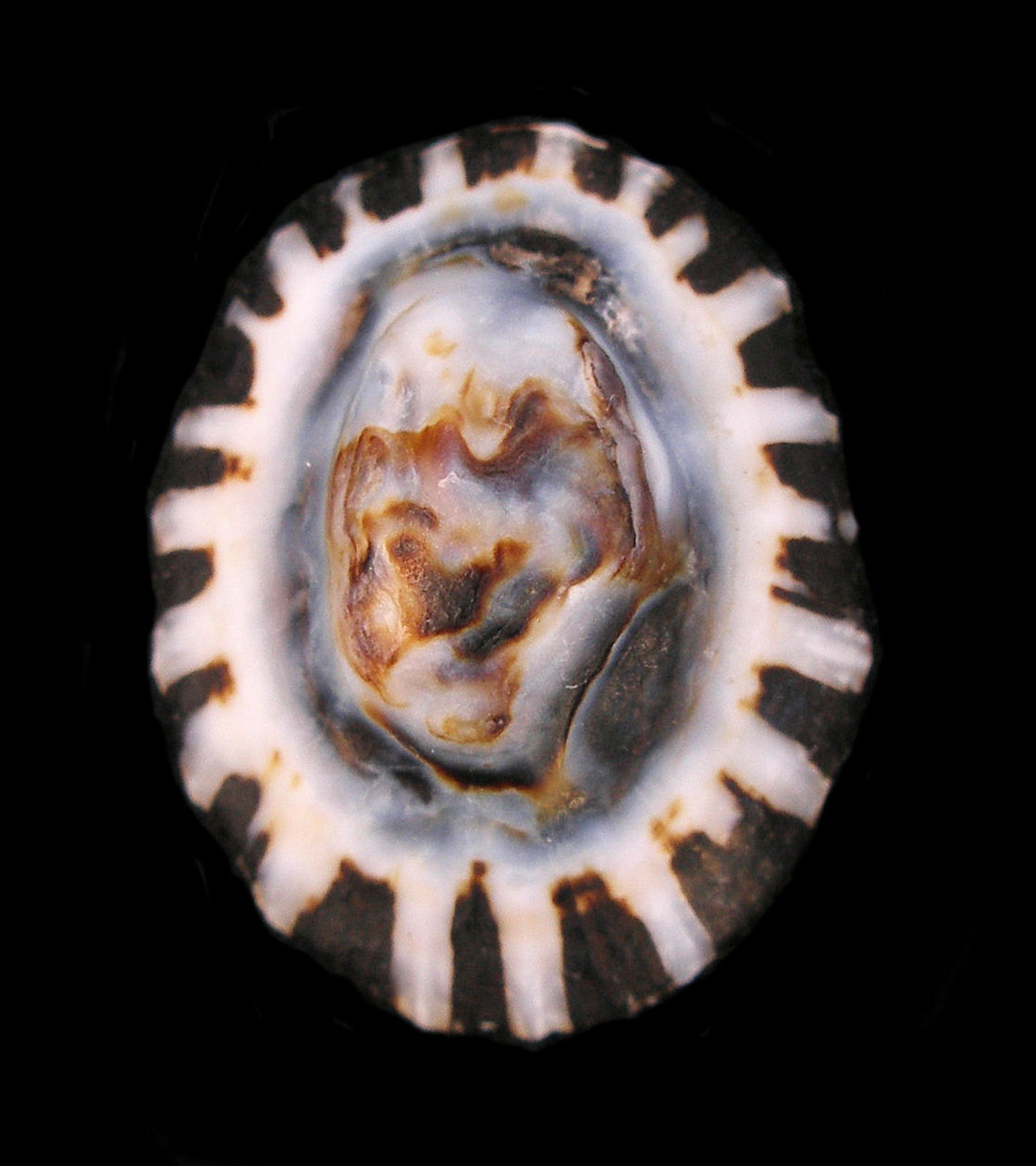
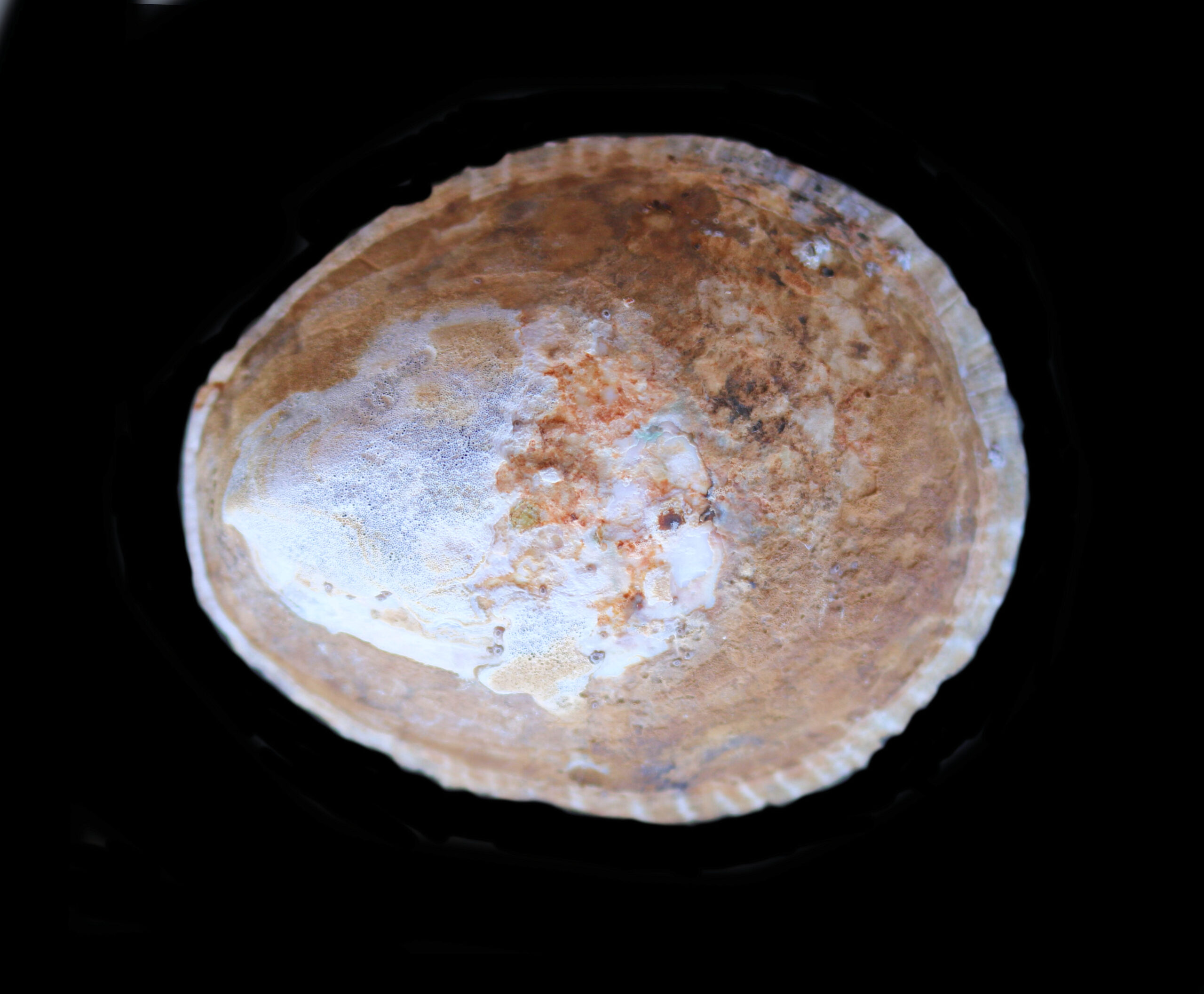 Owl Limpet Shell, Lottia gigantea
Owl Limpet Shell, Lottia gigantea