Keen’s Hairy Triton Shell, Monoplex keenae
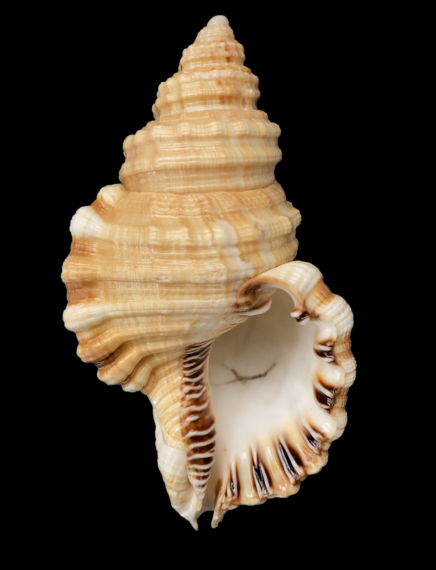
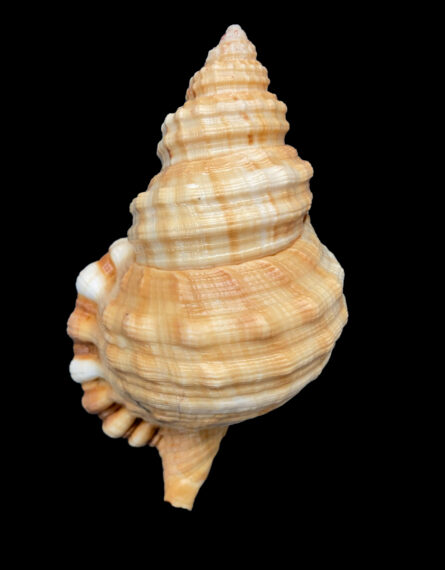
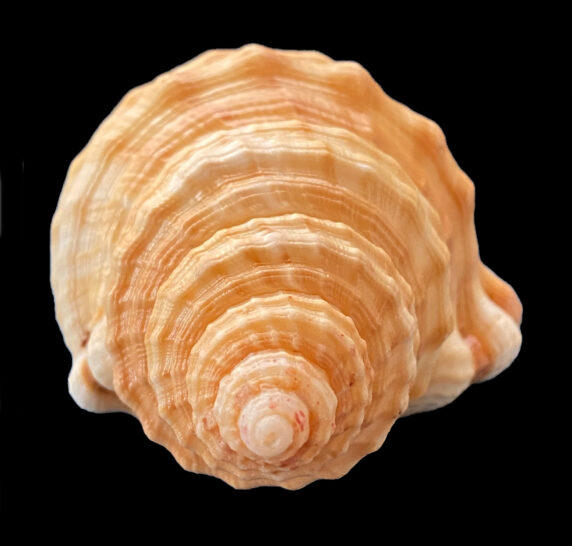

 Keen’s Hairy Triton Shell, Monoplex keenae. Shell collected off the beach at Punta Chivato, Baja California Sur, March 2022. Size: 13.4 cm (5.3 inches) x 7.6 cm (3.0 inches) x 6.2 cm (2.4 inches). Collection, photographs and identification courtesy of Colin Campbell, DVM, Punta Chivato, Baja California Sur.
Keen’s Hairy Triton Shell, Monoplex keenae. Shell collected off the beach at Punta Chivato, Baja California Sur, March 2022. Size: 13.4 cm (5.3 inches) x 7.6 cm (3.0 inches) x 6.2 cm (2.4 inches). Collection, photographs and identification courtesy of Colin Campbell, DVM, Punta Chivato, Baja California Sur.

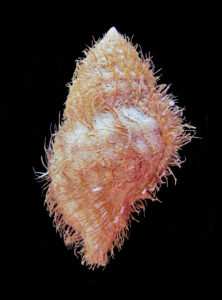 Keen’s Hairy Triton Shell, Monoplex keenae. Shell collected off the beach in the greater Bahía de los Ángeles area, Baja California, May 1992. Size: 13.8 cm (5.4 inches) x 7.9 cm (3.1 inches). Collection, photograph and identification courtesy of Bob Hillis, Ivins, Utah.
Keen’s Hairy Triton Shell, Monoplex keenae. Shell collected off the beach in the greater Bahía de los Ángeles area, Baja California, May 1992. Size: 13.8 cm (5.4 inches) x 7.9 cm (3.1 inches). Collection, photograph and identification courtesy of Bob Hillis, Ivins, Utah.
Phylogeny: Keen’s Hairy Triton, Monoplex keenae (Beu, 1970), is a gastropod mollusk that is a member of the Cymatiidae Family of Triton Shells. The genus Monoplex is one of twenty-three genera in this family, and there are twenty-seven species in this genus. In Mexico this species is called Cymatium de Keen.
Description: Keen’s Hairy Triton shell is thick and heavy with a spindle-shaped outline. The exterior is marked with thick spiral ridges and strong varices. It has a large aperture, which has a thick outer lip that contains wide, double-teeth, and an interior lip that is narrow with ridges. The exterior of the shell is cream to light brown in color, with darker brown axial lines and light brown, dark brown or white sections on the varices that cover the body whorl. Both the inner and outer lips of the aperture are dark brown and white in color. The siphonal canal and interior of the shell are white. This shell is covered with a yellowish-brown “hairy” periostracum. Keen’s Hairy Triton shells reach a maximum of 15.5 cm (6.1 inches) in length and 8.9 cm (3.5 inches) in height. Keen’s Hairy Triton is very similar to and is often confused with the Giant or Neapolitan Hairy Triton, Monoplex parthenopeum, which has a global distribution but is not found in the Eastern Pacific Ocean.
Habitat and Distribution: Keen’s Hairy Tritons reside on and within sand substrate, and are often found between rocks in the intertidal zone, and to depths up to 40 m (130 feet). They are a subtropical to tropical Eastern Pacific species that are found in Mexican waters of the Pacific Ocean from Magdalena Bay, Baja California Sur south to Guatemala. In the Gulf of California, they are found south of Mulegé, Baja California Sur.
Ecology and Behavior: Keen’s Hairy Tritons are a poorly studied and understood species. There is very limited documentation of their diet, predation, reproduction or ecosystem interactions. Other species in Family Cymatiidae are predators that feed primarily on bivalves, gastropods, ascidians, sea cucumbers, sea stars, and urchins. They sense their prey with chemoreceptors and utilize chemicals in their saliva to anesthetize and pre-digest their prey. In turn they are preyed upon by crabs, fish, sea stars, and predatory mollusks. Keen’s Hairy Tritons are gonochoric and reproduce sexually, through broadcast spawning, with external fertilization. Triton species are generally known for having a long larval phase. Consequently, they can drift, as plankton, for long distances before settling to the bottom. There is no mention in the available literature of them engaging in any types of parasitic, commensal, or symbiotic relationships. From a conservation perspective they are considered to be of Least Concern.
Synonyms: Cymatium (Monoplex) parthenopeum keenae and Septa (Monoplex) parthenopea keenae.